Fatshedera is one of the most popular hybrid plants among gardeners, obtained by crossing ordinary ivy and Japanese fatsia. The combination of qualities of these representatives of the fauna made the liana tolerant of almost any conditions, and its evergreen leaves can decorate every home.

Description
Young plants of this species have smooth and easily bent stems, which are covered with hard and rough bark at a more mature age. Since Fatshedera is a vine, it often needs support for active growth, because sometimes the height of the trunk reaches 5 meters! Vine leaves are divided into 3-5 parts and have a dark green color. There are representatives with a lighter frame.
The flowering period falls at the end of summer or beginning of autumn. Then flowers of tender pastel colors appear on the branches. Fruits a small-sized plant with berries of various shades of blue.
Varieties
In nature, there is only one species of this genus - Fatshedera Lise. But there are many varieties of the variety, their main difference is the color of the sheet plate:
| Grade | Feature |
| Variegata. | The foliage has a dark green color, and the veins and edges are light beige. |
| Silver prince. | The name itself indicates that the leaves of silver are painted green with a silver tint. |
| Pia. | It has wide and durable leaves with white edges. |
| Ennmike. | Lightens colors toward the center. The edges of the sheet often take an emerald color, and the core is whitish. |
| The star of Angio. | There are shades of green and beige palette on the foliage. |
| Aurea. | The core of the leaf plate is pale green, towards the edges the green becomes darker. |
| Aureopikta. | It differs in relatively small leaves with a bright green base color. |
| Lemon and lime. | Spotted dark green leaf with spots of different light shades. |
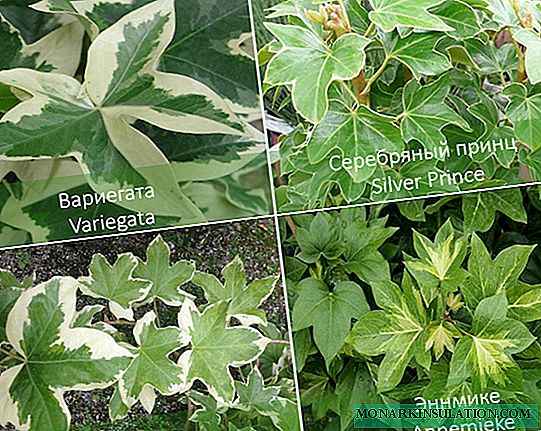
There are a lot of varieties, so you can choose the one that most harmoniously flows into the environment, after evaluating the variety from the photo.

Home Care
Since ivy is one of the ancestors of Fatschedera, this plant is unpretentious, and its cultivation does not require special gardening skills. However, it is worthwhile to adhere to some rules in order to get a beautiful and healthy green friend in your home.
Location, lighting, temperature, humidity
| Location | Lighting | Temperature | Air humidity | |
| Winter. | Cool place (balcony, porch, windowsill). | A bright place without direct sunlight (eastern or western windowsill). | +10… +16 | He likes moist air, in summer you need to spray with warm water from a spray bottle, wipe the leaves. |
| Summer. | In the fresh air without wind. | +20… +22 |
Planting, soil, pot
For planting, you can purchase soil with an acidity of pH 6-7. Experienced gardeners often use self-prepared mixtures in the proportions of 2: 2: 1: 1 of the following components:
- peat, turf, river sand and leafy soil;
- leafy soil, turf, pieces of pine bark and coarse sand.
Mixtures can be diluted with humus. A hybrid can grow completely without soil, then it is replaced by nutrient solutions.
The pot for planting needs to be selected in large sizes, since the vine has a well-developed root system. There must be holes at the bottom to drain excess fluid. So that the weight of the shoots does not overturn the container, you need to dig in 1/3 of the strong support. You can wrap it with a roll of moss, then its appearance behind the foliage will not violate the aesthetics of the tree. The shoots are attached to the support with threads or soft wire.
The pot and its contents are changed annually in the spring or as needed.
The plant requires more space, otherwise Fatshedera may receive less nutrients and begin to wither.
Watering
The frequency of watering depends on the time of year. In summer, an indoor vine is watered much more often than in winter. You can determine the need for hydration by the state of the soil: it should dry by about half, then you can water the plant again.
Great attention is paid to watering, especially in an apartment, since transfusion threatens to rot the root system, and an insufficient amount of water will cause the green pet to dry. Both of these cases are fatal to the fatalsheader.

Top dressing
In the period of active growth (spring and summer), the hybrid needs to be fed. Usually, a mix of complex and organic fertilizers is used for this, alternating them every decade. In winter, during hibernation, there is no need to introduce additional nutrition.
Formation, reproduction
To propagate the fatsheder, you can use seeds, stalks, aerial layering or simply divide an existing bush.

Air lay
With the onset of heat (March-April), the trunk of the liana is cut, a small piece of sphagnum moss soaked in a nutrient solution or phytostimulator is applied to this place. “Compress” is wrapped with cling film or an ordinary bag, the “wound” is periodically ventilated to prevent drying. After some time, new roots appear in the incision, and when they reach a sufficient length and get stronger, the top with roots is cut off and it can be planted in a separate pot, provided with nutritious soil and a good drainage system.
Cuttings
The upper branches are cut and transplanted into separate pots filled with peat and sand (1: 1). The trim is covered by a bag or a cut bottle to trap moisture and keep warm. When the stalk gets its own roots, you can transplant it into a more spacious pot for further growth.
Bush division
Propagation should be done with a sharp and clean knife. The hybrid is completely removed from the pot; its root system is neatly divided. Plants are planted in different containers with good drainage. The place of separation should be sprinkled with activated carbon.
Seeds
Planting is carried out in a mixture of turf, humus and sand in the same amount per 1 cm. If you place the seed deeper, it may not sprout. The pot is covered with a package, the temperature inside should be about +18 degrees. A transplant is performed when the first shoots appear.
Diseases and Pests
Fatshedera is rarely affected by diseases, but if they begin to develop, the cause of this is most often a violation of the rules of care.
| Signs | Causes | Elimination |
| Leaves are yellow and lethargic. | Excess moisture. | Reduced watering, drying the soil. |
| Leaves are dry and fall off. | Lack of moisture. | Moisturize the soil and spray with water. |
| Fluffy plaque on the shoots. | The disease is gray rot. Low temperature with high humidity. | Removal of affected parts, treatment of the rest with antifungal agents. |
| Variegated plants lose their pattern. | Lack of sunlight. | Moving to a more lighted place. |
| There are brown spots on the leaves. | Sunburn. | Limit exposure to sunlight. |
Most often, the mealybug, spider mite and scutellum attack the vine.
| View | Signs | Elimination |
| Spider mite. | Black dots on the leaves, thin web on the shoots. | If there are few insects, thorough washing of the plant will help. If a lot - treatment with specialized chemicals. |
| Mealybug. | White coating. | |
| Shield. | The shell pest is brown. |
The faster measures are taken to eliminate the negative effects, the less damage will be done to the plant by pests and disease.
Superstition
For many years, Fatshedera has been a key figure in the minds of superstitions. Many people believe that an exotic hybrid steals the life force of household members, feeds on their positive emotions, literally drains life force from the owners, is an omen of death. The opposite effect of the sign has, if the liana is located outside the house, then it serves as a kind of shield for evil spirits and negative influences.
There is a belief that the plant repels men, they feel discomfort, feel a breakdown near the descendant of ivy, therefore they avoid close contact and even try not to be in the same room with the green man-hater.
Of course, these are only signs and superstitions, to which it is not at all necessary to listen. In fact, Fatshedera, in exchange for the minimum amount of time spent on it, gives its owner the opportunity to enjoy the beautiful view of its wide green leaves, elegant flower buds and bright berries.











