The word apricot is usually associated with a large, orange or orange-red, juicy berry. Few have heard of black apricots. Even fewer have seen and tasted it. What a miracle it is, where to see it, whether it is possible to grow it on your own site. Features planting and growing. The basic rules of care. How can he get sick and what kind of pests can be expected. How to deal with them. About all this below.
Grade description
The direction of selection for obtaining apricot varieties with black fruits formed completely by accident. Just once once spontaneously dusted two trees - ordinary apricot and cherry plum. Someone (who is now impossible to find out exactly) took a bone of the resulting unusual fruit and planted it in the ground. And this seed gave direction for a new kind of apricots of an unusual color. Since then, breeders from different - mostly warm - countries have received more than one variety of black apricot. One of them is Black Velvet.
The variety was obtained in the Crimea by free pollination of American black apricot and entered into the State Register in 2006 in the North Caucasus region.
The tree turned out not too tall, a crown of medium density, flat-round, sprawling. It grows very slowly, the average growth per season is only 15-20 cm.

Apricot Black velvet blooms late, so it’s not afraid of return frosts
It has excellent resistance to winter frosts, and the flowers tolerate return frosts well, in the event of a change in weather they do not fall. Surprisingly, the yield in such cases even increases.
Unlike frost resistance, drought tolerance is average, therefore it requires watering.
Black velvet is partially self-fertile, therefore, to increase productivity it is good to have pollinators in the neighborhood. Cherry plum, plum, and thorns can play their role.
After 3-4 years, after planting, you can expect the first berries.
In the southern regions, the crop ripens in mid-July, further to the north - in early August.
The fruits of Black Velvet are larger than cherry plum berries, but smaller than the apricot (25-35 g), round-oval in shape and black-violet in color. The peel resembles velvet to the touch. The berry has a small but poorly detachable bone. This quality went to the hybrid from cherry plum. The pulp is red, juicy, sweet-sour, very pleasant taste, has a light aroma of apricot.

Apricot Berries Black velvet black-purple, with velvety skin
Good transportability. Collected slightly immature, berries can be stored in a ventilated cellar for 3-4 months.
It has an important advantage - good resistance to the main types of fungal diseases.
Planting apricot varieties Black Velvet
If the gardener wants to plant this apricot in his home, so that in subsequent years he will surprise neighbors and friends with an unusual berry, then first of all he needs to choose a suitable place. Protected from cold northerly winds, a well-lit place in the south or south-western part of the site, on a small slope - this is the best option for planting apricot Black Velvet.
In addition, the place should not be moist, and the soil should be acidic. In heavy soil, apricot will grow, but will not please the crop, so it is better to find a plot with looser earth for it.
And we must not forget about the neighbors who pollinating apricot will contribute to the formation of a large number of ovaries, and, as a result, to a high yield. If they are not, then partially self-fertile Black velvet is better not to plant.
If the landing site is chosen, then you need to take a few steps.
- Choose a landing time. In the southern regions, you can plant both in spring and autumn. In the more northern regions, in the Middle lane, including in the suburbs, there is a risk that a weakly rooted seedling, without gaining strength, may undergo severe frosts in the winter, which it cannot tolerate on its own. It’s necessary to take measures to warm it and it’s not the fact that this will certainly work. Therefore, consider spring planting. The best period is when the sap flow has not yet begun, but the soil has already begun to warm up.
- Buy sapling. But this is better to do in the fall. At this time, the quality of planting material is always better, because in the spring those seedlings that were not sold in the fall are usually sold in the leftovers. And it is not known in what conditions they were stored. When choosing a seedling, one should give preference to an annual or two-year-old plant with a well-developed root system.

Choose a one or two year old seedling with a well-developed root system
- Lay the seedling for winter storage in the basement with a temperature of 1-5 ° C. Before laying, dip the roots into the talker, which is prepared from clay and mullein in a ratio of 1 to 1. Then wrap it in a wet rag or burlap and put it in a plastic bag that cannot be completely covered so that the seedling can breathe.
- Prepare the landing pit as follows:
- Dig a round (with a diameter of 80 cm) or square (80 by 80 cm) pit, with a depth of 80 cm. The topsoil is then folded separately.
- Pour into the pit a nutrient mixture consisting of
- postponed digging of the upper fertile soil layer;
- humus or compost in the amount of 3-4 buckets;
- superphosphate in an amount of 300 g;
- wood ash in an amount of 2-3 liters.

The nutrient mixture is poured into the prepared hole
- Cover the hole with a waterproof material (film, roofing material, etc.) to avoid leaching of nutrients.
- In the spring, it remains only to form a mound in the pit, on which to place the root neck of the seedling, with the roots neatly straightened and covered with earth. Fill in small layers, carefully compacting the ground. Better to carry out this operation together. When planting, you need to pay attention to the fact that the root neck does not protrude above the ground. It needs to be deepened by 3-5 cm, and in sandy loam soil by 10-12 cm. At the same time, the vaccination site should not be buried, but not less than 5 cm above the ground.

Fill in small layers, carefully compacting the ground
- After planting a seedling, around it you need to form a tree trunk and pour enough water to soak all the loose soil and the roots are well enveloped by it.

The seedling is abundantly watered and mulched.
- Trim the seedling so that 60-80 cm is left and there are at least 4-5 growth buds on it.
If you bought an apricot seedling with a closed root system in a bag or container, then you can plant it at any time from April to October. But do not keep it in a container without special need - the sooner it is in a constant place, the better it will winter.
The subtleties of growing and caring
Like most apricot varieties, Black Velvet is unpretentious, and its standard care is reduced to watering, top dressing and pruning. And yet it does not hurt to refresh in memory the basic techniques and rules. Especially for beginning gardeners, this will be especially useful.
When and how to water apricot Black Velvet
This variety, as noted above, is not drought tolerant enough, but it does not like dampness and high humidity. It follows that you need to water it often, but not too profusely. It will be enough to water once every two weeks for 2-3 buckets under a young (up to 3-4 years) tree. With the onset of fruiting, the dose is slightly increased. In hot weather, it is advisable to irrigate the crown of the tree by sprinkling. The day after watering, the soil around the tree needs to be loosened to give oxygen access to the roots.
Top dressing
The first four years, the apricot does not need fertilizers, since they were sufficiently introduced during planting. In the fifth year, when the tree had already grown enough, it began to bear fruit and the nutrient reserves in the planting pit were depleted, we need to start feeding.
Table: types of fertilizers for apricot Black velvet, quantity and timing of application
| Fertilizer | Application rate | Dates and frequency |
| Humus, compost | 5 kg / m2 | Autumn digging, once every three years |
| Ammonium nitrate | 20 g / m2 | Every spring |
| Mullein infusion 3 l per bucket of water Infusion of bird droppings 1,5 l per bucket of water Infusion of freshly cut grass 5 kg per bucket of water After a week, one of these infusions is diluted with water 1 to 5 | 5 l / m2 | Immediately after flowering and two more times with an interval of 2 weeks |
| Superphosphate | 30 g / m2 | Annually in the autumn under digging |
| Boric acid | 0.2% solution | During flowering, leaf processing to increase the number of ovaries |
Apricot pruning
Pruning any tree, including apricot, is the most important agricultural technique. Typically, apricot uses the following types of pruning:
- formative
- sanitary
- regulatory.
Formative crown trimming
Is the most important. It is she who lays for many years the correct structure of the crown, its height, uniformity of filling of the internal space. As a result, this increases productivity, facilitates the care and harvest.
Most often, when forming a crown, a sparse-tiered formation is traditionally used. Every experienced gardener is familiar with it, the methods of its creation are described in many sources.
Recently, a new and promising form of the crown has appeared, which is called the "bowl" or "vase". It has certain advantages - uniform illumination of the tree and restraint of growth. This shape is perfect for apricot black velvet. The order of its creation is as follows.
- The first step was taken while planting - a seedling was cut to a height of 60-80 cm.
- Then you need to select 4 good, multidirectional buds, starting from the top of the seedling so that the distance between them is about 15 cm. All buds below the selected ones are blind.
- If the formation was started late, at the age of three, then the three best shoots are left, the remaining ones are cut "into the ring." The central conductor is cut into the upper kidney (shoot).
- In subsequent years, it is necessary to support the growth of skeletal branches so that they are equivalent and not one of them goes forward, becoming the central conductor. For this purpose, shoots are cut so that their tops are in the same plane.
- All shoots growing inside the crown are regularly cut.
- Two branches of the second order with a distance between them of 50-60 cm are formed on each skeletal branch.
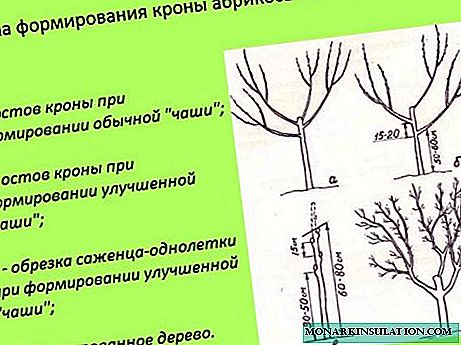
Bowl crown shape is the best option for Black Velvet
This completes the formation of the crown, from then on, the hacksaw will no longer be required, and all unnecessary shoots that arise, growing inside the crown, can be easily removed by secateurs.

Bowl shaped apricot crown great for Black Velvet
Annual shoots, if you tie them to the stakes and give a horizontal position, densely overgrown with fruits and give a greater harvest.
Sanitary and regulatory trim
Held regularly as needed. Sanitary, as usual, consists in the removal of dry, damaged and diseased branches. Regulating - in the removal of shoots and tops growing inside the crown, translation of shoot growth outward. And also in the summer they trim one third of the annual shoots (embossing), which stimulates lateral branching, on which a large number of flower buds will form next year.
Cropping Rules
All types of trimming should be carried out in compliance with certain rules.
- Only sharpened tools are used - saws, knives, pruners.
- Before cutting, the tool is disinfected with antiseptics - 1% solution of copper sulfate, alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, etc.
- When pruning branches, you can not leave hemp. If the branch is removed completely, the slice is carried out “on the ring”. Cutting off the annual shoots, leave the wood 0.5-1 cm above the upper bud.
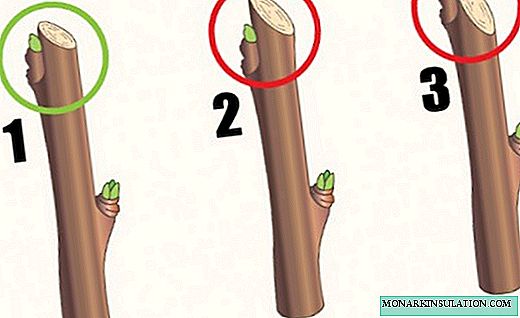
1 - correct pruning of the shoot; 2 - too much of the shoot is left above the kidney; 3 - the slice is too close to the kidney
- Slices are covered with a thin layer of garden varnish or garden putty based on natural materials such as lanolin or beeswax.
When buying a garden vare, you should give preference to one that does not contain refined products. The best basis for a garden var - natural, for example, beeswax, lanolin.
Features of growing apricot Black velvet in the suburbs
Although initially this exotic newcomer was regionalized in the North Caucasus region, he quickly (although not broadly) settled throughout the Middle Strip, including the Moscow Region. This was due to its high frost resistance, and especially the resistance of flower buds to return frosts due to late flowering.
In general, growing this apricot does not require any extraordinary methods and techniques from Muscovites. These are the usual, familiar to them tricks that apply to other cultures coming from the south of the country.
- Pre-winter water-loading irrigation.
- Autumn sanitary pruning.
- Shelter of young trees with various materials from frost - spanbond, roofing felt, film mini-greenhouses, etc.
- Lime whitewash of boles followed by roofing felt to protect against hares.
- Insulation of the trunk circle with mulching with straw, sawdust, etc., followed by snow cover up to a height of 60 cm. With the onset of spring thaws, snow needs to be removed from the trunks to avoid aging, which is often subject to apricots.
- In the spring, you need to carefully examine the tree bark for the detection of frost pits, which often appear during temperature jumps. If cracks are found, they are cleaned with a sharp knife and steel brush to a healthy bark, treated with 1% solution of copper sulfate and covered with a thin layer of a garden var.
Diseases and Pests
Apricot Black velvet, fortunately, is highly resistant to the main apricot trees, diseases and pests. Therefore, usually standard preventive measures are sufficient.
Preventive actions
In early spring and late autumn, every gardener carries out sanitary and preventive work in the garden, the composition of which is the same for many trees, including Black Velvet apricot.
Autumn events:
- Rake all the fallen leaves in heaps and burn them.
- Conduct sanitary pruning.
- If necessary, they clean the bark and bleach trunks and skeletal branches with lime. Such whitewashing will protect the bark of the tree from sunburn.
- Digging trunk trunks. As a result of this operation, pests wintering in the upper layers of the soil appear on the surface and die from frost.
- Wrap tree trunks with ruberoid so that the hares can not nibble the bark.
Spring Activities:
- The roofing material is removed, snow is removed from the trunks and the trees are inspected for possible damage.
- If necessary, carry out sanitary pruning.
- Spray with complex preparations to protect the tree from pests and diseases:
- BOTTOM,
- Nitrafen
- 3% solution of copper sulfate,
- 5% solution of iron sulfate,
- 3% solution of Bordeaux mixture, etc.
Both autumn and spring, preventive measures are carried out in the absence of sap flow.
How can Black Velvet get sick?
As already mentioned above, subject to basic preventive measures, this apricot is most likely not to get sick. But in life everything can be. In the spring, the gardener for some reason did not spray with protective preparations, and even did not remove last year's foliage. This is where some fungus can attack. Most often these are the following diseases.
Moniliosis
The disease develops only if there is dampness, high humidity. Often in spring, spores of the fungus are introduced by bees. Through a flower, moniliosis spreads to leaves and young shoots. The affected plant looks like it is burnt. This explains another name for the disease - a monilial burn. Affected shoots must be immediately cut into 30 cm of healthy wood.

This is how apricot leaves affected by moniliosis look like.
If the disease develops in the summer, then apricot berries are affected. First, black dots appear on them, then gray rot.

Black dots appear on the berries affected by moniliosis.
After the apricot blossoms and during the ripening period, systemic fungicides (antifungal drugs), for example, Horus or Quadris, are used. Treatments are carried out regularly, every two weeks, but no more than three times with one drug. These drugs are addictive and further processing by them does not make sense. Eating fruits is allowed after 3-5 days with the use of Quadris and after 7 days with Horus.
Coccomycosis
Usually this disease begins to appear in late May or early June. On the outside of the leaves, small spots of red-brown color form. If spraying with a fungicide is not carried out immediately, the disease will progress. By mid-July, outgrowths in the form of pads of gray, white and pink colors will appear on the underside of the leaves. Inside the growths are spores of the fungus. In August, if nothing is done, it will be possible to observe a phenomenon such as summer leaf fall. With severe damage, the fruits and shoots also suffer. The tree is very weak and may not tolerate winter.

Seeing the black dots on the apricot leaves, you need to immediately start processing with fungicides
Timely and regular treatment with fungicides will certainly protect the gardener from this scourge. Strobi, Fitosporin-M, Fundazol, Horus, Quadris is far from a complete list of drugs that will help in the spring and summer.
Kleasterosporiosis
This disease is also called hole perforation. So it is called due to the fact that as a result of leaf damage, colored (often reddish-brown) spots grow to sizes of 8-12 mm, then their inner part dries and spills out, forming holes. Due to the very short incubation period (only 2-3 days), the disease begins and proceeds very quickly. Depending on humidity, the period from the moment a fungal spore enters the plant until the formation of holes on the leaves can take from 10 to 15 days. More than one generation of the fungus develops during the season, causing significant damage to the tree, especially since in addition to the leaves, the fungus affects the buds, flowers, ovaries, and fruits.

Holes on apricot leaves may appear as early as 10-15 days after infection with spores of kleasterosporiosis
To combat this disease, all the methods and preparations described above are suitable.
Who can attack Black Velvet
Apricot has few pests. And just as in the situation with diseases, prevention warns against their attack by almost 100%.
Weevil beetle
There are many varieties of this dangerous insect in nature. And many of them are not too picky in food - they attack any plants, including those that can enjoy young buds, flowers, ovaries, and apricot leaves. In winter, they hide in the bark of trees, fallen leaves and topsoils. Early in the spring they crawl out of the shelters and climb the crown of the tree. If it is cold outside and the temperature does not exceed 5-10 ° C, then the beetles at that time sleep, sitting still on branches. This feature is used to manually collect pests. Early in the morning, a fabric or film is spread out under the crown, after which the beetles are gently shaken off from each branch. Collected weevils are destroyed.

Weevil named this beetle for its long proboscis
Then, the tree should be treated with insecticides, for example, Decis, Fufanon, etc.
Beetles that did not turn out to be hand-picked and survived during processing lay eggs in the soil. In June, 4–6 mm larvae crawl out of the eggs. They can eat young roots of the tree, which also cause damage to it.

Weevil larva can feed on young tree roots
You can resist them at this time. To do this, at the end of May, under digging, you need to make 5-10 g / m2 Diazonin Its validity is 20 days, during this time most of the larvae will die. The drug does not accumulate in the soil and does not get into the fruit.
Khrushchev
These are the larvae of May and some other bugs. They are larger than the weevil larvae (individual species reach 35 mm), respectively, and more noticeable damage can cause. With a massive defeat, young seedlings can die or weaken greatly.

The larvae of the well-known May beetle have a size of 20-25 mm
In addition to soil treatment with diazonin-based preparations, you can also try making bait near the tree. You need to pour a small mound of humus or compost, moistening it well with water. Cover with a black film or roofing material to maintain heat. Larvae will be happy to climb into a warm, humid place, from where they are subsequently manually collected and destroyed. And also slugs can crawl into this pile if they are on the site. Of course, they will face the same fate as the Khrushchev.
Reviews
Black velvet is pleasant because it is cold-resistant and disease-resistant. When frosts beat other varieties of apricots, this one usually survives, because it is a hybrid of apricot and cherry plum. But the taste of apricot. And it bears fruit in August, when other apricots have already hatched. And large - up to 40-60 g. And partly self-fertile! Other varieties of black apricot are smaller. And the compote from it is cool (I don’t know the jam - I didn’t cook it). Well, that's why I decided to take two - and Prince and Velvet. Black velvet is even more stable, but it is not large, simpler than the Prince. Every apricot can get sick and freeze, not all are 100% tenacious, but black is still more stable than ordinary ones. I saw photos of black apricots grown in Siberia, boasted at the gardening forum. True, they are small there and do not gain color.
Alikavikt
//chudo-ogorod.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?t=975
Black apricot feels good in central Russia, is frost-resistant and has a high resistance to fungal diseases of stone fruits. Later flowering of these plants helps to avoid loss of ovaries during spring frosts. Thanks to these qualities, as well as pleasant taste and unusual appearance, black apricot varieties are becoming more and more popular.
Winnie the Pooh
//www.forum-volgograd.ru/showthread.php?t=255937
Apricot Black velvet, like other black apricots, got good frost resistance and disease resistance when crossed. Due to these qualities, the area of its cultivation expanded to the north and reached the suburbs. But the quality of the fruits decreased, they became smaller, the seeds began to separate worse, the taste acquired acid. Therefore, this hybrid has not found wide distribution and is grown mainly because of its exotic color.

















